Which Animal Phylum Is Largest In Terms Of Numbers Of Individual Organisms?
What is Animal Classification?
Animal kingdom classification is an important organisation for understanding how all living organisms are related. Based on the Linnaeus method, species are arranged grouped based on shared characteristics.
This system of animal kingdom nomenclature was adult by Swedish botanist Carolus (Carl) Linnaeus in the 1700'south. The Linnaeus Method, besides known as Linnaean Taxonomy, creates a hierarchy of groupings called taxa, also every bit binomial nomenclature that gives each animal species a ii-word scientific name. This method of giving scientific names to animals is typically rooted in Latin past combining the genus and species. For case, humans are classified as homo sapiens while wolves are canis lupus.
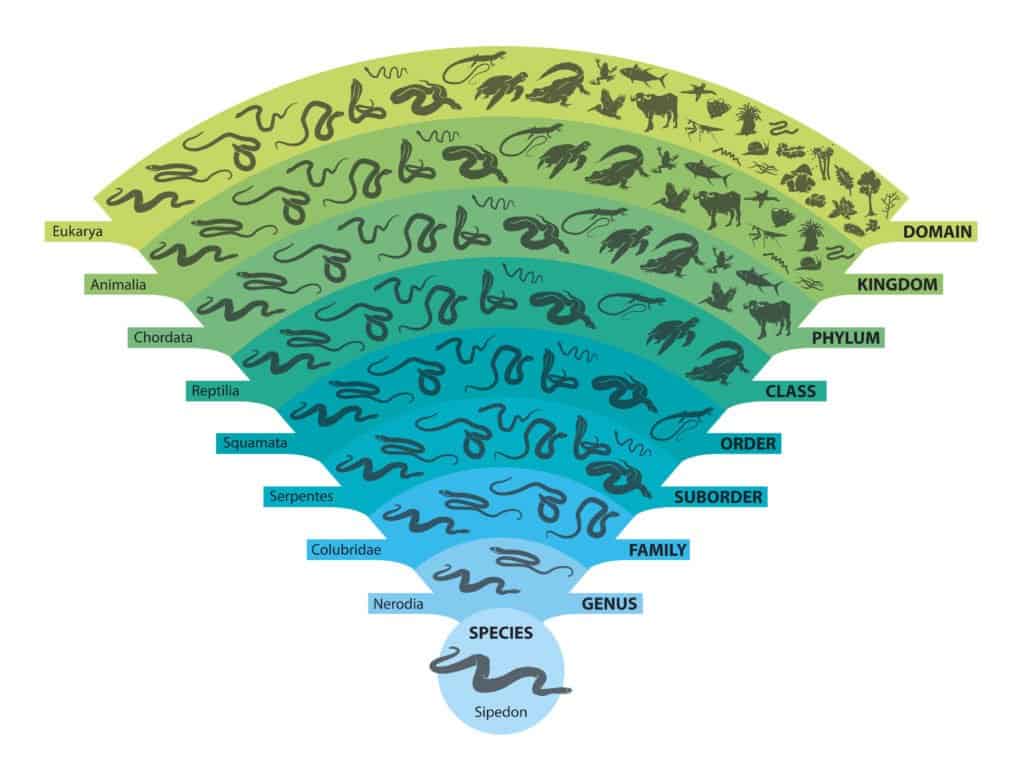
The more features that a group of animals share, the more than specific that animate being classification grouping is. Every species is defined based on nine branching categories. The master method of animal nomenclature is:
- Domain
- Kingdom
- Phylum
- Class
- Lodge
- Suborder
- Animal Families
- Genus
- Species
EreborMountain/Shutterstock.com
Animal Nomenclature: The Six Different Fauna Kingdoms
All living organisms tin can be placed in 1 of six dissimilar animal kingdom classifications. The characteristics of each beast kingdom are:
- Beast – A kingdom of complex multi-celled organisms that practise not produce their own food. This kingdom contains all living and extinct animals. Examples include elephants, whales, and humans.
- Plants – Circuitous and multi cellular autotrophic organisms, meaning they produce their own food through photosynthesis. Examples include trees, flowers, and grass.
- Fungi – Multi-celled organisms that do non produce their own food, unlike plants. Examples include molds, mushrooms, and yeast.
- Protista – Unmarried celled organisms with more than complexity than either eubacteria or archaebacteria. Examples include algae and amoebas
- Eubacteria – Single celled organisms institute in everything from yogurt to your intestines. This kingdom contains all bacteria in the earth not considered archaebacteria.
- Archaebacteria – The oldest known living organisms. Single-celled and found in hostile and extremely hot areas like thermal vents or hot springs
Fauna Phylums Explained
After animal kingdom, animal species unremarkably autumn into one of seven different phylum, or phyla:
- Porifera – Marine animals more commonly known as sponges and establish in every body of water on earth.
- Cnidaria – By and large marine animals that include over 11,000 species. Examples include coral, jellyfish, and anemones
- Platyhelminthes – Typically parasitic flatworms. Lacking in any respiratory or circulatory systems, oxygen pass through their bodies instead in a process known every bit diffusion. Examples include tapeworms and flukes.
- Annelida – More complex than Platyhelminthes, these are segmented and symmetrical worms containing a nervous system, respiratory organisation, and sense organs. Examples include the common earthworm and leeches.
- Mollusca – The 2d largest phylum by species count, and the largest marine phylum. Invertebrates with soft unsegmented bodies. Information technology is estimated almost a quarter of marine life fall in this category. Examples include clams, mussels, and snails
- Arthropoda – Invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton and segmented bodies. Contains insects, crustaceans, and arachnids. This is the largest phylum by species count. Examples include scorpions, butterflies, and shrimp
- Chordata – Vertebrates. Animals that develop a notochord, a cartilaginous skeletal rod that supports the trunk in embryo and tin often become a spine. Nearly animals we are familiar with, including dogs, horses, birds, and humans autumn in to this category.
Brute Classes
The phylum group is then divided into even smaller groups, known equally animal classes. The Chordata phylum splits in to these 7 creature classes:
- Agnatha (jaw-less fish)
- Chrondrichtyes (cartilaginous fish)
- Osteichthyes (bony fish)
- Amphibia (amphibians)
- Reptilia (reptiles)
- Aves (birds)
- Mammalia (mammals)
Different Animal Orders
Each class is divided into small-scale groups once more, known as orders. There is no universally accepted breakdown for the class Mammalia. Some outline as many as 26 different orders for the class mammalia. Some of the most pop examples include:
- Artiodactyla (even-toed hoofed animals) – Examples include moose, camels, and giraffes
- Carnivora – Animals that specialize in more often than not eating meat, but also contains some omnivores and herbivores. Characterized as having nonretractable claws and long snouts. Examples include bears.
- Rodentia (gnawing mammals) – Examples include beavers, mice, and squirrels
- Chiropptera (bats) – The only mammals that tin fly. Examples include free-tailed and vampire bats
- Cetacea (porpoises and whales) – Examples include killer whales, dolphins, and hump-backed whales
- Primates – Includes prehensile hands and feet, normally with opposable thumbs. Examples include gorillas, chimpanzees, and humans.
Animal Families
In every club, there are unlike animal families which all accept very like features. The Carnivora order breaks into animal families that include Felidae (Cats), Canidae (Dogs), Ursidae (Bears), and Mustelidae (Weasels).
Animal Genus Types
Every animal family is farther divided into small groups known as genus. Each genus contains animals that have very similar features and are closely related. For example, the Felidae (Cat) family contains genus including Felis (modest Cats and domestic Cats), Panthera (Tigers, Leopards, Jaguars and Lions) and Puma (Panthers and Cougars).
Fauna Species Names
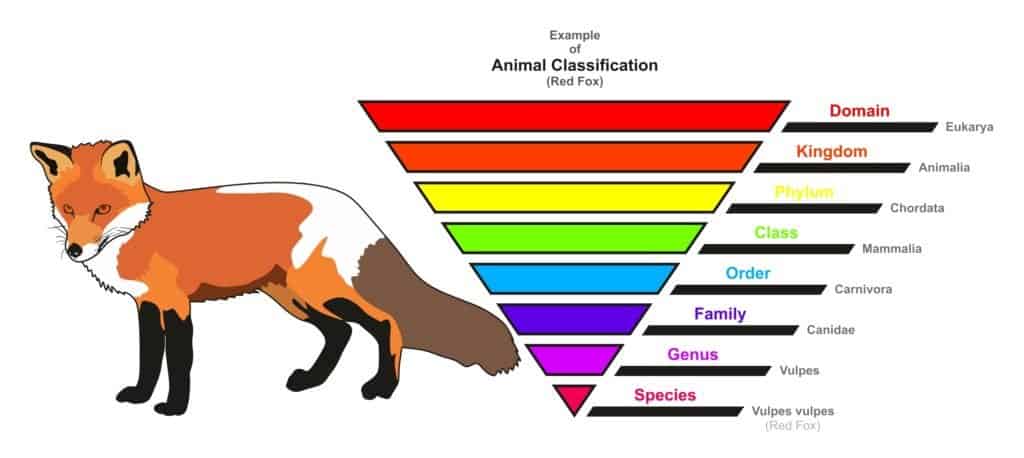
Each individual species within the genus is named after its private features and characteristics. The names of animals are based in Latin and consist of two words. The first word in the name of an animal will be the genus, and the second name indicates the specific species. This method of organizing scientific names of animal species was developed by Carl Linnaeus in the 1700's. Equally an example, a dolphin species proper noun is Delphinus Delphis. A red fox is Vulpes vulpes. This brute classification chart of a red play a joke on is an example of Linnaean Taxonomy
udaix/Shutterstock.com
Animate being Classification Example one – Red Pull a fast one on
- (Vertebrate)
- Class: Mammalia (Mammal)
- Order: Carnivora (Carnivore)
- Family: Canidae (Domestic dog)
- Genus: Vulpes
- Species: Vulpes vulpes (scarlet play tricks)
Brute Classification Example two – Orang-utan
- Kingdom: Animalia (Animal)
- Phylum: Chordata (Vertebrate)
- Class: Mammalia (Mammal)
- Order: Primates
- Family: Hominidae (Neat Apes)
- Genus: Pongo
- Species: Pongo pygmaeus (Orang-Utan)
Source: https://a-z-animals.com/reference/animal-classification/
Posted by: smiththeyet.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Which Animal Phylum Is Largest In Terms Of Numbers Of Individual Organisms?"
Post a Comment